Climate
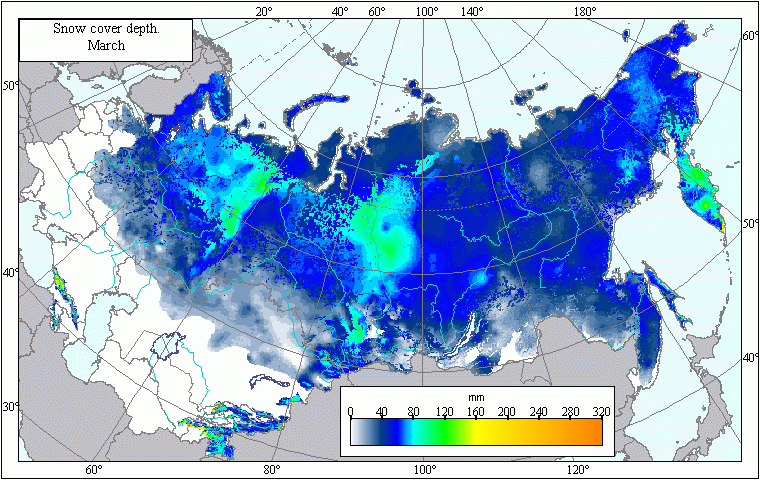
Map of snow depth in March .
 Download GIS-layers
Download GIS-layers
Authors:
Afonin, A.N., Lipiyaynen, K.L., Tsepelev, V.Y.Compilation date:
14.03.2005.Scale:
10 km/pixMap's precision:
The map contains the averaged mean annual values of snow depth in March for patches of the earth's surface with an area of 10 x 10 km.Projection:
"Albers Equal Area for the USSR":ref. system : Albers Equal Area Conic for Russia
projection : Albers Equal Area Conic
datum : Pulkovo 1942 (S42)
delta WGS84 : 28 -130 -95
ellipsoid : Krasovsky
major s-ax : 6378245.000
minor s-ax : 6356863.019
origin long : 100
origin lat : 0
origin X : 0
origin Y : 0
scale fac : na
units : m
parameters : 2
stand ln 1 : 44
stand ln 2 : 68
Main content:
A bitmapped map containing mean annual values of snow depth in March.Classifier precision:
Snow depth is expressed in centimeters within a 5-cm margin of error.Map compilation procedure:
The map has been compiled using observations of snow depth taken by member stations of the weather station network within the former USSR. The mean average snow depth values were taken from climate reference books (Climate Handbooks of the USSR, 1965-1974). Data from 2851 weather stations have been used in the compilation process. The bitmapped temperature layer was created using Kriging.s climate simulation technique (Hart et al., 1996). The influence of seas and other large bodies of water on snowfall was taken into account. Thus, the mapping process dealt with the coastal and mainland weather stations separately. All weather stations located less than 30 km away from the coast were considered coastal. Snow cover's redistribution is greatly influenced by forests. Therefore, map compilation procedures took into account the presence or absence of woods. Snow depth measurements taken in the woods have been used to map woodland snow levels. Wooded and woodless lands were distinguished using a template derived from the USSR Forest Map (Garsia et al., 1990). The main factors taken into consideration during mapping were the stations. altitudes above sea level, as well as their latitude and longitude. Compilation procedures also involved the calculation of the relationship between snow depth, average air temperature, and the amount of precipitation fallen during preceding periods during which temperatures were below zero (multiple linear regression). Previously created layers of average monthly air temperature and precipitation were used to elaborate the master snow depth layer (Afonin et al., 2006). The difference between actual and calculated values was the remainder, which was then interpolated over the whole scanned area according to the Kriging method. Snow depth's matrix was calculated using the Idrisi program (Image Calculator module) in accordance with the obtained regression formula, in which the corresponding matrices of latitude, longitude, altitude, temperature and precipitation were substituted for these parameters. The final compilation of the snow depth map involved the addition of the interpolated remainder's layer into the calculated layer.Data sources:
Afonin, A.N., Lipiyaynen, K.L., Tsepelev, V.Y. 2006. Precipitation Maps. In: Afonin, А.N.; Grinn, S.L.; Dzyubenko, N.I.; Frolov, А.N. The On-Line Atlas of Useful Plants Their Pests and Ecological Factors in Russia and Neighboring Countries [Internet-version 1.0]. St. Petersburg, Russia. St. Petersburg State University, Faculty of Geography. 2006, Jan. https://agroatlas.ru/Afonin, A.N., Lipiyaynen, K.L., Tsepelev, V.Y. 2006. Maps of Average Mean Annual Air Temperature. In: Afonin, А.N.; Grinn, S.L.; Dzyubenko, N.I.; Frolov, А.N. The On-Line Atlas of Useful Plants Their Pests and Ecological Factors in Russia and Neighboring Countries [Internet-version 1.0]. St. Petersburg, Russia. St. Petersburg State University, Faculty of Geography. 2006, Jan. https://agroatlas.ru/
Climate Handbooks of the USSR. Air and Soil Temperature. Issues 1-34. - Leningrad: 1965-1974.
Garsia, M.G., ed. 1990. Forests of the USSR (a 1: 2,500,000 map). Department of Forest Cartography of All-Union State Project and Survey Institute Soyuzghiproleskhoz. GUGK, Moscow.
Hart, T., Greene, S., Afonin, A. April, 1996. Mapping for Germplasm Collections: Site Selection and Attribution/ ASPRS Annual meeting in Baltimore, Maryland. Web-paper.
SRTM (Shuttle Radar Topography Mission) 3 arc second (90 meter) SRTM DTED(r) Level 1 "Finished" data derived from SRTM IFSAR data/ http://edc.usgs.gov/products/elevation.html

